Definition: Tax Planning can be understood as the activity undertaken by the assessee to reduce the tax liability by making optimum use of all permissible allowances, deductions, concessions, exemptions, rebates, exclusions and so forth, available under the statute.
In other words, it is an arrangement or method of an assessee’s financial transactions, in such a way that complete tax benefit can be availed or the tax implication can be minimised by legitimate means, i.e. taking benefit of all the beneficial provisions and relaxations provided in the income tax law, so that the incidence of the tax is minimum. This enables savings of taxes along with adherence to the legal compliances.
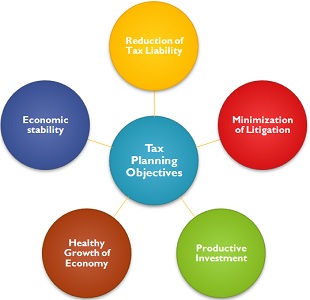
Objectives of Tax Planning
- Reduction of Tax: An assessee can save maximum amount of tax, by properly arranging his/her transactions within the framework of the statute.
- Minimization of Litigation: It is always a war-like situation between the tax collectors and taxpayers as the later wants the tax liability to be minimum while the former attempts to get the maximum. So, a proper tax planning aims at being complied with respect to applicable statutes, in such a way that incidence of litigation is minimized.
- Productive Investment: One of the major reason or outcome of tax planning is channelizing taxable income to different investment plans. It aims at the maximum resources available for productive investments and reducing the tax liability.
- Healthy Growth of Economy: The growth of the economy massively depends on the growth of its people. Tax planning measures involve generating more money that flows freely and results in the sound progress of the economy.
- Economic Stability: Tax amount savings are eventually ploughed back into economy with more investment in business – which would generate jobs and wealth or more expenses – again making other business prosper. Hence proper tax planning brings economic stability by various techniques such as mobilizing resources for national projects or availing ways for investments which are productive in nature.

Types of Tax Planning
- Short-range and long-range Tax Planning: The tax planning done with single year in mind to arrive at specific objectives, is called short-range tax planning. On the other hand, long-range tax planning looks at such practices undertaken by the assesseefor a period which goes beyond one year.
- Permissive Tax Planning: Planning made as per the provision of the taxation laws is termed as permissive tax planning.
- Purposive Tax Planning: Purposive tax planning refers to the tax planning method which misleads the law. Under this type, there is no expressed provision of the statute.
